
Complete Human Body 3D Model
Interactive 3D anatomy viewer to explore the skeleton, heart, and veins in lifelike detail.

Interactive 3D anatomy viewer to explore the skeleton, heart, and veins in lifelike detail.

If you’re a student, researcher, or knowledge enthusiast who spends hours hunting for clear, trustworthy information — we’ve built something just for you.
Meet the AI Research Assistant — an intelligent, friendly chatbot now live on research.help, powered by Google Gemini, one of the most advanced AI models in the world.

AI in Research 2025 Statistics. A recent survey found that over half of students and early-career researchers are already using AI tools for literature reviews (51%) and nearly as many for writing and editing (46.3%). In just a few years, AI has gone from a novelty to a necessity in academia.

A bedside monitor tracking a patient’s vital signs in an intensive care unit. AI-driven systems can analyze such data in real time to alert clinicians to conditions like sepsis hours earlier than traditional methods, helping save lives.Ai and Machine Learning in Healthcare rapidly reshaping healthcare.

When a deadly disease suddenly appears, epidemiologists spring into action like detectives chasing clues. Epidemiology, often called the “science of public health detectives,” investigates how diseases spread, who is affected, and how to stop them.

Human development is a lifelong journey of change. Developmental psychology is the branch of psychology that studies how people grow and adapt physically, mentally, and socially from conception through old age
positivepsychology.com
.

Overview:
This 7-day action plan is tailored for research.help, a site for researchers and students, to significantly boost web traffic within one week. The plan focuses on quick-win SEO improvements, immediate content creation, targeted social media outreach, email marketing, backlink opportunities, and other free/low-cost tactics. Each day has specific, actionable steps.

I’ve been fascinated by birds ever since I was a kid. There’s something magical about these creatures that never fails to take my breath away. Birds aren’t just animals – they’re living works of art flying right over our heads! From the mind-blowing colors of tropical species to the elegant dancers of the sky, our planet’s feathered residents offer some seriously jaw-dropping eye candy.
I’ve developed a powerful yet user-friendly statistical analysis tool that allows researchers, students, and data analysts to perform t-tests and calculate p-values directly in their browser. This tool requires no installation or advanced technical knowledge – simply upload your data and get meaningful statistical insights.

Currently, research.help has no affiliate partnerships or sponsored content. We do not earn commissions from external products or services, and we do not run advertisements.

Accessibility Statement
We are committed to making research.help accessible to all users, including people with disabilities.

Research.help is not designed for children, but we recognize that minors may access it. In compliance with COPPA (U.S.) and similar laws, we do not knowingly collect personal information from children under 13 without parental consentftc.gov.

All content on research.help (text, images, etc.) is either created by us or used with permission. It is protected by copyright.

Data Protection: We use industry-standard security measures to protect your data. All data transmissions to our site occur over secure HTTPS (TLS encryption).

research.help may include health or medical-related educational content, but this is not medical advice. We are not a substitute for professional healthcare.

All materials on research.help are for informational and educational purposes only. We do not guarantee any specific academic or professional results from using this content.

All content on research.help is free of charge. We do not sell subscriptions or memberships, so there are no charges to cancel.

What Are Cookies: Cookies are small text files stored on your device that help us recognize your browser and remember preferences. We use both first-party cookies (set by our domain) and third-party cookies (set by external providers). Third-party cookies enable features like analytics or (if applicable) targeted content. For example, we use “strictly necessary” cookies for basic site functions, and other cookies to understand user behavior and improve our servicetermly.iotermly.io.

Eligibility: research.help is open to all, but if you are under age 13, you should not provide any personal data (see Children’s Policy below). In the European Union, users must be at least 16 (or the age of consent in your country) to provide personal data without parental permission. By using this site, you confirm you meet the applicable age requirements or have parental consent.

Scope and Data Collected: research.help collects only what you provide voluntarily — your name and college email address (for the weekly newsletter). We do not require any other personal data to use the site. All data collection is opt-in(you choose to subscribe) and is limited to academic email addresses to verify student/research affiliation. We explain why we collect each piece of information when you submit it.
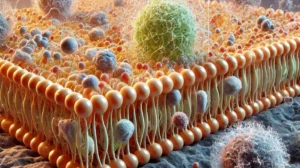
Observe how molecules of different sizes pass through a semi-permeable cell membrane. This simulates how cell membranes allow some substances to pass through while blocking others.

In the 1920s, Czech playwright Karel Čapek introduced the word “robot” in his play R.U.R. (Rossum’s Universal Robots). Derived from the Czech word “robota,” meaning forced labor, the term described artificial humans created to work in factories. A century later, robots and automation systems have transcended science fiction to become integral parts of our world—manufacturing our goods, exploring distant planets, performing delicate surgeries, and even vacuuming our homes.

For over 70 years, classical computers have transformed our world, enabling everything from space exploration to smartphones. These machines, regardless of their size or power, all operate on the same fundamental principle: processing bits of information that exist in one of two states—0 or 1. This binary approach has served us remarkably well, but we’re beginning to encounter problems so complex that classical computers would take impractical amounts of time to solve them—billions of years in some cases.

The human brain—a three-pound universe of approximately 86 billion neurons—remains one of the most complex and fascinating structures in existence. Despite centuries of study, we’ve only begun to understand how this remarkable organ creates our thoughts, emotions, memories, and consciousness itself. Neuroscience stands at this frontier, working to decode the intricate processes that make us who we are.

Imagine building a house on a foundation that slowly crumbles. No matter how beautiful the structure, it will eventually collapse. For generations, much of human development has followed this pattern—creating prosperity and technological advances while inadvertently undermining the very foundations that support our existence: ecological systems, social cohesion, and long-term economic stability.

For most of modern history, humanity has powered its remarkable technological progress primarily through fossil fuels—coal, oil, and natural gas. These energy-dense, convenient fuels enabled the Industrial Revolution and the unprecedented economic growth and quality of life improvements that followed. However, this progress has come with significant costs: climate change, air and water pollution, resource depletion, and geopolitical tensions.

Climate policy refers to the strategies, rules, regulations, and initiatives developed by governments, international bodies, and organizations to address climate change. These policies aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote adaptation to climate impacts, and transition to a more sustainable, low-carbon economy. Climate policies operate at multiple levels—international, national, regional, and local—and involve various sectors including energy, transportation, industry, agriculture, and forestry.

When we talk about a “carbon footprint,” we’re referring to the total amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs) generated by our actions. Although it’s called a carbon footprint, it actually includes various greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), nitrous oxide (N₂O), and fluorinated gases—all converted into a carbon dioxide equivalent (CO₂e) for simplicity of measurement. This concept helps us understand our individual and collective impact on climate change.

Protecting Our Planet, When we walk through a forest, snorkel over a coral reef, or simply look around a garden, we’re witnessing biodiversity—the immense variety of life on Earth.

Our planet is experiencing profound changes. The evidence is all around us—from shifting weather patterns and rising seas to declining biodiversity and deteriorating air quality. To understand these changes and work toward solutions, we need to understand two interconnected areas: environmental science and climate change.

Imagine having a crystal ball that could help you anticipate customer needs, identify potential risks, optimize resources, and make data-driven decisions with confidence. While actual fortune-telling remains in the realm of fantasy, predictive modeling offers the next best thing—a scientific approach to forecasting future outcomes based on historical data patterns.

In today’s data-driven world, we’re constantly surrounded by information. Organizations collect unprecedented amounts of data about customers, operations, markets, and more. But raw data—endless rows and columns of numbers—rarely tells a compelling story on its own. This is where data visualization steps in, transforming abstract numbers into meaningful visual insights that can be quickly understood and acted upon.

Data mining is like digging for gold in a vast digital landscape. Ever wondered how Netflix knows your next favorite show or how Amazon recommends just what you need? The answer lies in data mining—the art and science of extracting valuable insights from large datasets.

Math , science, history Quiz game

In today’s digital landscape, businesses are generating unprecedented volumes of data through various channels and touchpoints. However, the true value of this data lies not in its volume but in the insights it can yield when properly analyzed. Data analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data to discover meaningful patterns, correlations, and trends that can inform business decisions.

In today’s interconnected digital landscape, Big Data has emerged as a transformative force reshaping how organizations operate, compete, and innovate. Big Data refers to the exponentially growing volumes of structured and unstructured data that are too large or complex for traditional data processing applications to handle efficiently. What distinguishes Big Data is not just its sheer volume but also its variety, velocity, and veracity—characteristics that have come to be known as the “4 Vs.”

In today’s hyperconnected world, data is more than numbers—it’s a powerful asset fueling innovation across industries. At the heart of this revolution are two interconnected disciplines: Data Science and Big Data. Data Science blends statistical analysis, computer science, and domain expertise to uncover insights

In today’s hyperconnected digital landscape, network security has evolved from an IT concern to a fundamental business imperative. Network security encompasses the policies, practices, and technologies designed to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and accessibility of computer networks and data.

In a world where cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated and costly—averaging over $4.45 million per data breach—Information Assurance (IA) is no longer just a technical necessity. It’s a strategic priority.

Learn how modern threat intelligence turns raw data into proactive defense. Discover CTI types, tools, and best practices to outpace ransomware and APTs.

In our hyperconnected world, where data flows continuously across global networks, cryptography serves as the guardian of our digital lives. Cryptography—the science of securing information through codes and ciphers—has evolved from ancient secret writing techniques to sophisticated mathematical algorithms that protect everything from your banking transactions to private messages.

Blockchain technology has transformed numerous industries with its promise of decentralization, transparency, and immutability. However, as blockchain adoption accelerates across finance, supply chain, healthcare, and beyond, so do the security challenges associated with this revolutionary technology. Blockchain security encompasses the measures, protocols, and best practices designed to protect blockchain networks, smart contracts, and digital assets from unauthorized access, attacks, and vulnerabilities.

In today’s hyperconnected digital landscape, cybersecurity has evolved from an IT concern to a fundamental business and personal imperative. Cybersecurity encompasses the technologies, processes, and practices designed to protect networks, devices, programs, and data from attack, damage, or unauthorized access.

Navigate growth and digital change with expert consulting. Learn service types, benefits, vetting questions, and trends shaping the industry in 2025.

Synthetic biology is transforming how we understand and use life. At its core, it blends biology with engineering, allowing scientists to design and build new biological systems or reprogram existing ones.

Imagine a world where devastating genetic diseases are cured before symptoms appear, where crops can thrive in previously uninhabitable environments, and where microorganisms produce biodegradable plastics that eliminate pollution. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the emerging reality being shaped by biotechnology and genetic engineering.

Imagine a world where your medical treatment is as unique as your fingerprint—where medications are precisely tailored to your genetic makeup, where diseases are detected years before symptoms appear, and where prevention strategies are customized to your specific risk profile.

See how rapid, low-cost genomic sequencing is reshaping healthcare, farming, and environmental science—plus the privacy and ethics we must tackle next.

Discover how modern gene therapy is curing inherited diseases, reshaping cancer care, and opening ethical debates about editing our DNA—see what’s next in medicine.
Imagine a world where genetic diseases are relics of the past, where crops withstand extreme weather conditions without failing, and where personalized medicine is the standard, not the exception. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the burgeoning reality shaped by CRISPR-Cas9, the revolutionary gene-editing technology that has transformed biotechnology and genetic engineering practically overnight.

Explore how biotech and genetic engineering fuel precision medicine, resilient crops, green fuels, and CRISPR breakthroughs—plus the ethics guiding this revolution.

Reinforcement learning (RL) represents one of the most fascinating branches of artificial intelligence—a computational approach that mirrors how humans naturally learn through trial, error, and reward. Unlike other machine learning paradigms that require extensive labeled datasets, reinforcement learning agents discover optimal behaviors through direct interaction with their environments, making this approach uniquely powerful for solving complex, sequential decision-making problems.
In the vast landscape of artificial intelligence, few approaches mirror the human learning process as closely as reinforcement learning (RL). Unlike traditional programming where instructions are explicitly coded, reinforcement learning empowers machines to learn from their own experiences—their triumphs and failures—gradually refining their decision-making abilities through continuous interaction with their environment.

Natural Language Processing (NLP) stands at the fascinating intersection of linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence, enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. Unlike the rigid syntax of programming languages, human language is inherently ambiguous, context-dependent, and constantly evolving—making it one of the most challenging domains for computational systems to master.

Deep learning represents one of the most significant advancements in artificial intelligence over the past decade, enabling machines to learn complex patterns from vast amounts of data. Unlike traditional machine learning approaches that require extensive feature engineering, deep learning algorithms automatically discover representations needed for detection or classification directly from raw data. From voice assistants that understand natural language to autonomous vehicles navigating city streets, deep learning has transformed how we interact with technology and solve previously intractable problems.

Computer Vision (CV) represents one of the most transformative applications of artificial intelligence, enabling machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world. This technology attempts to replicate the complex processes of human visual perception, allowing computers to identify objects, recognize patterns, track movements, and extract meaningful information from images and videos. From self-driving cars navigating busy streets to medical imaging systems detecting early signs of disease, computer vision is revolutionizing how we solve problems across virtually every industry.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from a theoretical concept to a transformative force in our society. As these systems become more sophisticated and pervasive, they raise profound ethical questions about their development, deployment, and governance. AI ethics examines the moral implications of creating and using intelligent systems, seeking to ensure these technologies align with human values and contribute positively to society.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have transformed from abstract theoretical concepts to practical technologies that touch virtually every aspect of modern life. From the recommendations on your favorite streaming service to the autonomous vehicles being tested on our roads, AI and ML systems are increasingly becoming integral to how we interact with technology and with each other.
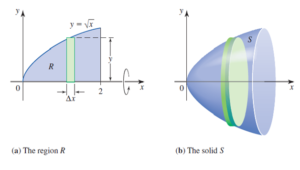
Welcome to the Solids of Revolution Visualization Tool – an interactive web‑based calculator designed to help students and educators explore volumes generated by revolving regions around an axis. Built using Babylon.js for 3D rendering and Math.js for function evaluation, this tool integrates real‑time calculations with dynamic visualization.

In our fast-paced digital world, finding effective ways to unwind and destress has become increasingly important. Bubble Pop, a simple yet engaging browser game, offers a surprisingly effective method for relaxation and mental refreshment. Let’s explore the psychological benefits of this satisfying digital activity and how it can become part of your mental wellness routine.

In today’s digital landscape, finding tools that blend artistry with technology can transform how we express ourselves online. The WebGL Fluid Simulation is one such remarkable tool that puts the mesmerizing power of fluid dynamics at your fingertips. Whether you’re a designer seeking unique backgrounds, a content creator looking for eye-catching visuals, or simply someone who appreciates digital art, this simulation offers endless possibilities.

This study explores the potential of Human-AI Collaboration (HAIC) use cases as a tool for prospective sensemaking. Based on 14 interviews with executives of an automotive company, we identify and categorize HAIC use cases that can help organizations anticipate and strategically respond to the impact of HAIC.